The narratives of 1921, 2008, and 2020 are still in full effect after two years of pandemic disruption in the housing market. All the threats of eviction, homelessness, and systemic racism are still present, with the potential to worsen, in 2022.

For a brief moment in time, in those first fevered weeks and months of the Covid-19 pandemic, rents dropped in the United States. But with so many renters struggling to make ends meet and reports of an urban exodus making daily headlines, relief from the market hardly seemed like enough good news to overcome the worst fears about the pandemic.
Now a new report from the authoritative source on the rental market proves that the early pandemic decline in rent prices is over. "Rental housing demand came roaring back in the second year of the pandemic, reducing vacancy rates and driving up rents," according to the "America’s Rental Housing 2022" report released late last week by the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies (HJCHS).
Digging deeper into the data reveals the sadly familiar story of lower-income renters, and especially lower-income renters of color, bearing the brunt of the rental housing market. The report finds that nearly a quarter of Black renters and 19 percent of Hispanic renters were behind on rent in the third quarter of 2021. Eighteen percent of Asian renter households were in arrears during the same time period. The share of white renter households, however, was only 9 percent.
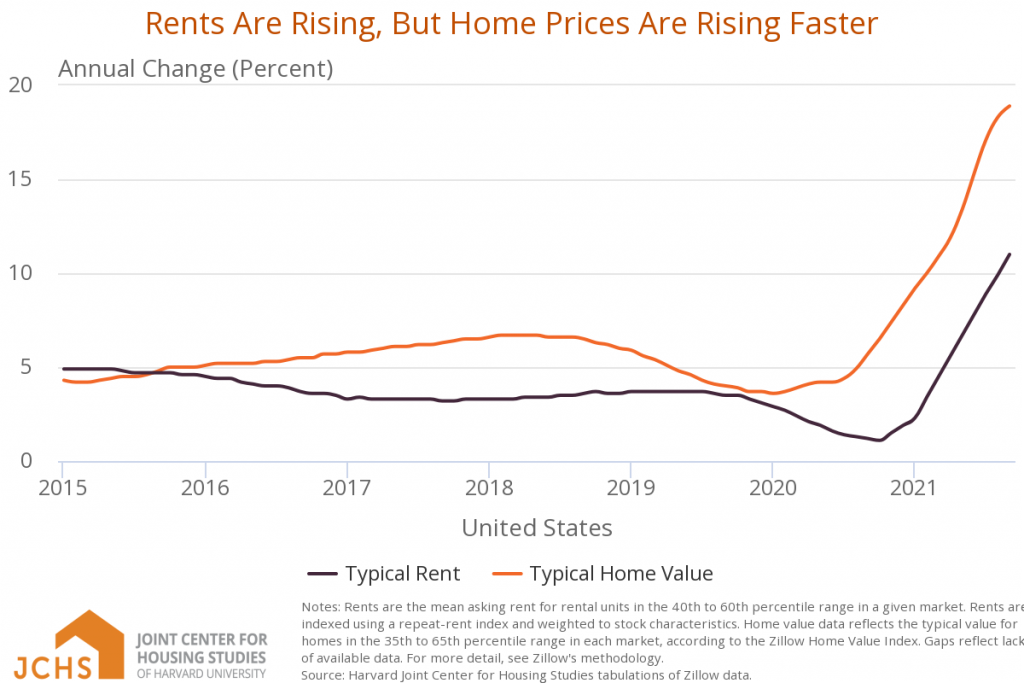
The effects of the rental market are reminiscent of the rental market during and after the Great Recession. In 2022, it's a historic shortage of inventory and record price increases in the for-sale market instead of foreclosures driving new demand to the rental market.
The risk of the pandemic exacerbating the nation's ongoing crises of evictions, homelessness, and systemic racism have not been eradicated—far from it. From data reported earlier in the pandemic, we know that evictions contributed to tens of thousands of deaths during the pandemic and that thousands of people experiencing homelessness died from Covid-19 in the streets.
The data in the 2022 rental housing report should raise alarms about the future and dispel any notion that the economic recoveries since the early pandemic have been evenly or sustainably applied. When published in 2020, the same report predicted that housing affordability challenges would soon spread to cities not usually listed among the most expensive in the country—a trend that became painfully obvious in the past year.
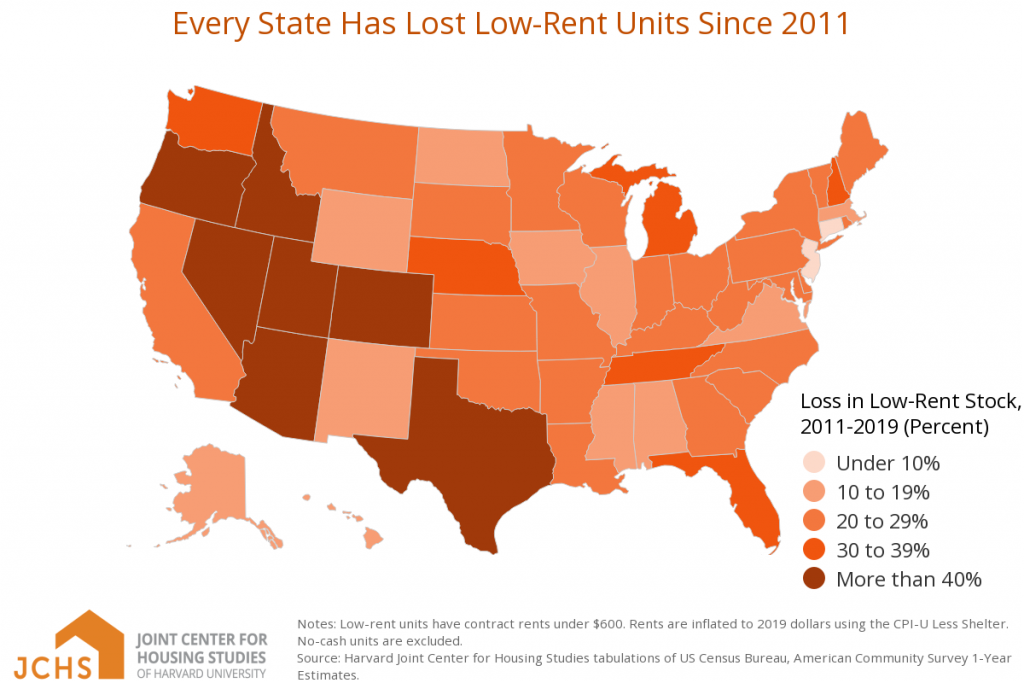
The "America's Rental Housing 2022" reports many of the same trends it's reported in the past, despite the outlier of 2020. Renters in 2022 continue to have higher incomes just like they did in 2020. The increasingly wealthy renter population is competing for record low supply—the number of units renting for less than $600 fell by 3.9 million between 2011 and 2019. The report also presents evidence that 870,000 renter households were created between the first quarter of 2020 and the third quarter of 2021. An estimated 44 million U.S. households now rent.
Wall Street has mobilized to take advantage of the growing number of renters in the market—buying up housing supply and, some say, contributing to scarcity in the for-sale housing market. Numerous jurisdictions around the country are mobilizing their zoning codes (Massachusetts, most recently) to provide more opportunities for multi-family development, but the consequences of these planning reforms will play out on timelines extending into the next decade and beyond, and nothing is certain.
In the meantime, an unrelenting string of research like "America's Rental Housing 2022" presents evidence that the U.S. housing market—aided and abetted by the institutions and individuals of the planning profession—is driving downward economic and social mobility.

Planetizen Federal Action Tracker
A weekly monitor of how Trump’s orders and actions are impacting planners and planning in America.

Map: Where Senate Republicans Want to Sell Your Public Lands
For public land advocates, the Senate Republicans’ proposal to sell millions of acres of public land in the West is “the biggest fight of their careers.”

Restaurant Patios Were a Pandemic Win — Why Were They so Hard to Keep?
Social distancing requirements and changes in travel patterns prompted cities to pilot new uses for street and sidewalk space. Then it got complicated.

Platform Pilsner: Vancouver Transit Agency Releases... a Beer?
TransLink will receive a portion of every sale of the four-pack.

Toronto Weighs Cheaper Transit, Parking Hikes for Major Events
Special event rates would take effect during large festivals, sports games and concerts to ‘discourage driving, manage congestion and free up space for transit.”

Berlin to Consider Car-Free Zone Larger Than Manhattan
The area bound by the 22-mile Ringbahn would still allow 12 uses of a private automobile per year per person, and several other exemptions.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Heyer Gruel & Associates PA
JM Goldson LLC
Custer County Colorado
City of Camden Redevelopment Agency
City of Astoria
Transportation Research & Education Center (TREC) at Portland State University
Camden Redevelopment Agency
City of Claremont
Municipality of Princeton (NJ)






























