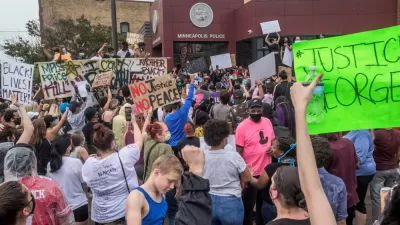As biking gains popularity as a transportation mode during the pandemic, planners are called on to elevate the role of "invisible cyclists"—people of color on bikes—in the process of redesigning and re-engineering streets.

An article by Julian Agyeman, professor of Urban and Environmental Policy and Planning at Tufts University, calls on city planners, lawmakers, and bike advocates to better address and remove barriers to cycling for people living in poorer neighborhoods, in a time when more and more people are using the bike as a primary mode of transportation.
Design-related, infrastructural challenges, such as providing more bike lanes, or better still, protected bike lanes – paths separated from both road and sidewalk – are important. But the more fundamental barriers are political, cultural and economic in nature. Failure to acknowledge and act accordingly, risks compromising the ability of low-income and minority groups to enjoy the full benefits of cycling.
The article details the history of bike advocacy, which has tended to produce outcomes in keeping with the whiteness of its constituency—bike lanes have face criticism as a harbinger of gentrification along the way, for example. But according to Agyeman, who provides evidence to back this claim, there are many people of color who also advocate for safe bike infrastructure, they just go "unrecognized, underreported and unrepresented."
"Cyclists of color tend to miss the eye of city planners, but the same can’t be said of the law," according to Agyeman, who provides plenty of evidence that people of color on bikes are policed in a completely different way than white people on bikes. This is one of the discriminatory facts of life in the public realm that advocates argue will perpetuate racial inequality in planning for ostensibly progressive causes like bike infrastructure and traffic safety.
"As cities reimagine their streets in a post-pandemic world, politicians, city planners and bike advocates could better recognize that cyclists have differing status, rights, needs and capabilities depending on their social and racial background," according to Agyeman.
FULL STORY: Poor and black ‘invisible cyclists’ need to be part of post-pandemic transport planning too

Maui's Vacation Rental Debate Turns Ugly
Verbal attacks, misinformation campaigns and fistfights plague a high-stakes debate to convert thousands of vacation rentals into long-term housing.

Planetizen Federal Action Tracker
A weekly monitor of how Trump’s orders and actions are impacting planners and planning in America.

In Urban Planning, AI Prompting Could be the New Design Thinking
Creativity has long been key to great urban design. What if we see AI as our new creative partner?

King County Supportive Housing Program Offers Hope for Unhoused Residents
The county is taking a ‘Housing First’ approach that prioritizes getting people into housing, then offering wraparound supportive services.

Researchers Use AI to Get Clearer Picture of US Housing
Analysts are using artificial intelligence to supercharge their research by allowing them to comb through data faster. Though these AI tools can be error prone, they save time and housing researchers are optimistic about the future.

Making Shared Micromobility More Inclusive
Cities and shared mobility system operators can do more to include people with disabilities in planning and operations, per a new report.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
planning NEXT
Appalachian Highlands Housing Partners
Mpact (founded as Rail~Volution)
City of Camden Redevelopment Agency
City of Astoria
City of Portland
City of Laramie