Introducing car sharing (ZipCar, Hertz Connect, etc,) to a development can significantly reduce parking demand and, hence, construction costs.
Introducing car sharing (ZipCar, Hertz Connect, etc,) to a development can significantly reduce parking demand and, hence, construction costs.
There are about ten studies on car sharing that relate, to varying degrees, membership in a car share club to the choice of no longer owning a car. Surveys of members, data from existing programs, and empirical evidence from several developments have shown that when a car share vehicle is available in a convenient location and, usually, combined with transit access, a significant number of people make a decision that it is no longer necessary to own a car. These studies are performed with varying objectives using different criteria; however, a reasonable standard to measure the impact the above relationship has on a development is the ratio of car share vehicles to households that voluntarily forfeit individual car ownership. While the conversion is not uniform across all studies, an acceptable ratio identified in the various samples seems to range from six to twenty-three. Some studies forecast that as car sharing becomes more prevalent (and competitive), this ratio could perhaps double. An interesting side benefit, albeit not studied as much, is the effect car sharing has on total number of vehicle trips generated by a development, since car club members consider the cost of hopping in the car on the fly, as opposed to the sunk cost of car ownership that pays out the more you drive.
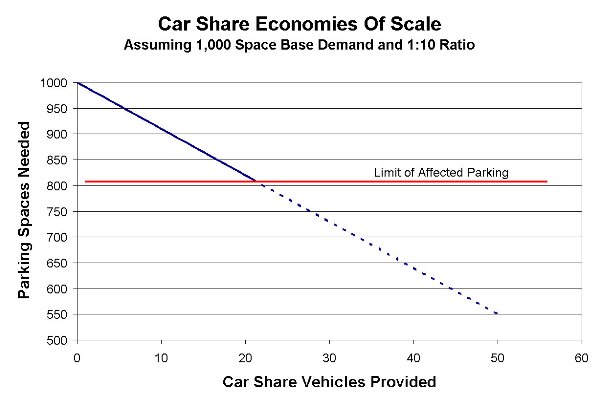
Another way to look at the above ratio is the number of parking spaces that can be eliminated for each car share vehicle provided. Since parking demand is a function of the number of spaces required per unit of development, any urban residential or mixed-use development with sufficient transit access can expect to reduce the total number of parking spaces demanded if a car sharing program is made available. For example, a development located adjacent to a major transit hub with a calculated base parking demand of 1,000 spaces can apply an appropriate ratio within the range given above, say 1:10, to estimate that for every car share vehicle provided, ten parking spaces can be removed (it's actually nine spaces because one space for the car share vehicle is still needed). So, providing five car share vehicles would reduce parking demand by fifty spaces, for a net reduction of 45 spaces.
The graph below represents the above exercise while increasing the number of car share vehicles from two to fifty. The 1:10 ratio is used here, but choosing the appropriate ratio is an exercise in engineering judgment that typically involves both empirical data from acceptable comparables and negotiations with local zoning officials. Note that at some point, the provision of additional car share vehicles is not only unprofitable for the car share club, but also fails to further reduce parking demand. This can be considered the limit of affected parking demand. For this demonstration, a limit of twenty car share vehicles is identified; however, the true value for this threshold is more accurately defined by the car share club's finance staff.
It's important to note that I say car sharing "program" above because sprinkling car share vehicles nearby or even on site is typically not enough realize an appreciable reduction in private vehicle ownership. Rather, the developer must market car sharing as a feature, include incentives such as subsidized membership fees, and collaborate with the car share club to select the proper mix of car models for the development (Trump recently included BMW, Jaguar, and Mini ZipCars at his new Jersey City luxury high-rise).
While the most applicable use for this new concept is in urban areas with readily available transit service, I believe similar benefits can be gained from use of car share vehicles in more suburban situations as well. An example is a subdivision street where ten or twenty households each own a second or third car that rarely gets used. Placement of a car share vehicle to be shared amongst a critical mass of households may significantly reduce the total number of vehicles needed in that community.

Planetizen Federal Action Tracker
A weekly monitor of how Trump’s orders and actions are impacting planners and planning in America.

Chicago’s Ghost Rails
Just beneath the surface of the modern city lie the remnants of its expansive early 20th-century streetcar system.

Amtrak Cutting Jobs, Funding to High-Speed Rail
The agency plans to cut 10 percent of its workforce and has confirmed it will not fund new high-speed rail projects.

Ohio Forces Data Centers to Prepay for Power
Utilities are calling on states to hold data center operators responsible for new energy demands to prevent leaving consumers on the hook for their bills.

MARTA CEO Steps Down Amid Citizenship Concerns
MARTA’s board announced Thursday that its chief, who is from Canada, is resigning due to questions about his immigration status.

Silicon Valley ‘Bike Superhighway’ Awarded $14M State Grant
A Caltrans grant brings the 10-mile Central Bikeway project connecting Santa Clara and East San Jose closer to fruition.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Caltrans
City of Fort Worth
Mpact (founded as Rail~Volution)
City of Camden Redevelopment Agency
City of Astoria
City of Portland
City of Laramie




























